The Integrity of FIFA, the Reforms You Must Know
February 2016 is a month that FIFA and the entire world would never forget due the corruption crisis that rocked FIFA. In February, the FIFA President, General Secretary and UEFA President were ousted from office due to corrupt practices and banned. After the crisis FIFA pledged to implement and roll down a lot reforms. On 26 February 2016, Gianni Infantino was elected as FIFA President for a term of three years and he pledged to implement the reforms. The FIFA reforms are based on four thematic areas which are Governance, Transparency, Accountability and Diversity.

In this article, SportsGoogly will discuss the major reform decisions that you need to know. FIFA has a responsibility to adapt to the latest developments in the world of football to ensure that its operations and values adhere to the best governance standards possible. Over the past 15 years, FIFA has progressively adopted a wide range of governance reforms that reflect the views of the football community in order to meet the evolving needs of the modern game. FIFA wishes to achieve the reforms by implementing the four thematic through the following;
 • Clear separation between “political” and management functions: The FIFA Council (replacing the FIFA Executive Committee) is responsible for setting the organization’s overall strategic direction, while the General Secretariat oversees the operational and commercial actions required to effectively execute that strategy.
• Clear separation between “political” and management functions: The FIFA Council (replacing the FIFA Executive Committee) is responsible for setting the organization’s overall strategic direction, while the General Secretariat oversees the operational and commercial actions required to effectively execute that strategy.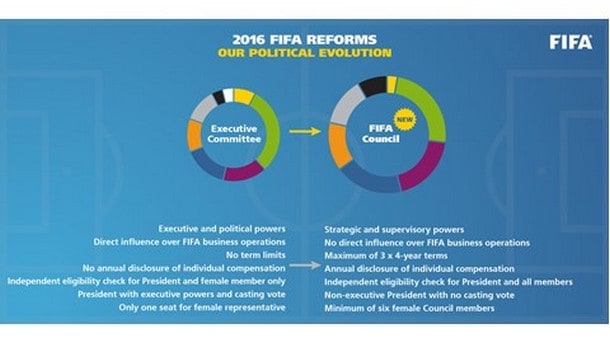
- Term limits for the FIFA President, FIFA Council members and members of the Audit and Compliance Committee and of the judicial bodies (maximum of 12 years).

- Election of Council members: supervised by FIFA and in accordance with FIFA’s own electoral regulations; all candidates subject to comprehensive eligibility and integrity checks conducted by an independent FIFA Review Committee.

- Greater recognition and promotion of women in football: with a minimum of one female representative elected as a Council member per confederation; promotion of women as an explicit statutory objective of FIFA to create a more diverse decision making environment and culture.

- Disclosure of individual compensation on an annual basis of the FIFA President, all FIFA Council members, the Secretary General and relevant chairpersons of independent standing and judicial committees.
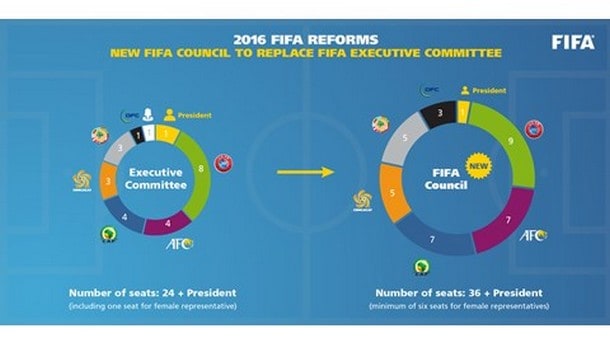
- Enhance control of money flows.

- Universal good governance principles for confederations and member associations.

- Human Right: FIFA’s commitment to human rights to be enshrined in the FIFA Statutes.

- New Football Stakeholder Committee to ensure greater transparency and inclusion through broader stakeholder representation (including players, clubs and leagues).
After the implementation of these key strategic reforms, this is how new FIFA will look like;
The President

The FIFA President holds the highest office at FIFA. He is elected for four years by those member associations represented at the FIFA Congress who are eligible to vote and he can also be re-elected. The FIFA President’s rights and duties are set forth in the FIFA Statutes. He represents FIFA and presides over the FIFA Congress, Executive and Emergency Committee meetings and those committees of which he has been appointed chairman. Like the other members of the FIFA Executive Committee, he is entitled to vote and he casts the deciding vote when a ballot is tied.
FIFA Congress

According to the statutes, the FIFA Congress is the organization’s supreme body. Numerous articles dictate which items are to be discussed and which decisions are to be passed at this forum. As the legislative body of world football – football’s parliament in other words – the Congress bears a particular responsibility for developing the game, the nature of which has been subject to increasingly rapid change over the past few years. Each member has one vote at the Congress.
Committees
Although football remains a simple game, its circumstances have changed dramatically. As the world governing body, FIFA must take into account a wide range of developments and other factors and decide on numerous issues in accordance with the FIFA Statutes and regulations.
Strategy is determined by the FIFA Executive Committee chaired by the FIFA President, a forum where all of the confederations can directly influence the decision-making process since each has its own representation under the FIFA Statutes. The executive’s decisions are guided by the recommendations of some 22 specialist standing committees, in which representatives from the confederations and associations are able to express their various views and requirements. The FIFA administration implements the decisions passed by the FIFA Congress, the executive and the standing committees.
Ethics Committee
To ensure a separation of powers, the independent Ethics Committee, established as the third judicial body under the FIFA Code of Ethics, is responsible for watching over the entire football community and helping to tackle current challenges in football such as illegal betting, bribery and other prohibited activities. Under the Code of Ethics, disciplinary sanctions can be imposed on offending officials, players, players’ agents and match agents.

Concluding, if FIFA is able to implement and complete the reforms, football administration around the world and at FIFA will be free and devoid of conflicts of interest, political interference and zero tolerance for discrimination.


